Precise threading is essential in manufacturing. For engineers, machinists, and designers, understanding the difference between inch and metric thread sizes is vital for accurate machining. This guide explores these standards, ensuring you’re well-equipped to choose the right thread type for your project.
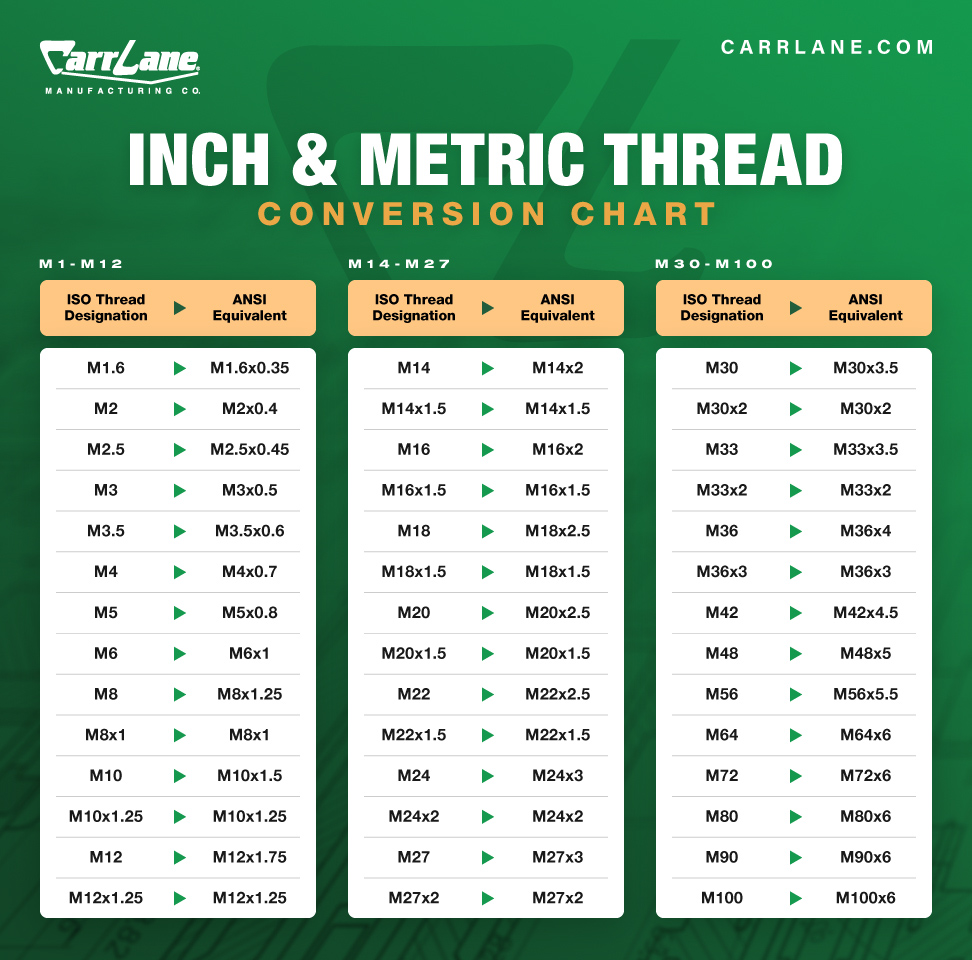
Understanding the conversion between ISO and ANSI standards is vital for professionals frequently dealing with both systems. Below, we’ve included a conversion chart that compares the ISO thread designation to its ANSI equivalent. This handy tool is perfect for quick reference and ensures accuracy in your threading choices.
Understanding Inch & Metric Thread Callouts
Inch thread sizes are typically specified using the nominal major diameter and the number of threads per inch. The nominal major thread diameter refers to the theoretical diameter of the thread measured from crest to crest across the outside of the male threads or inside the female threads. It is essentially the largest diameter of a screw thread. Take, for example, a 3/8-16 (coarse) thread. It has a 3/8" nominal major diameter and 16 threads per inch. On the other hand, a 3/8-24 (fine) thread, while having the same nominal major diameter, offers 24 threads per inch, providing a finer, more closely packed threading.
Metric threads play by different rules. They are specified using thread pitch, which is the distance between threads in millimeters. For instance, an M10x1.5 (coarse) thread boasts a 1.5mm pitch, whereas an M10x1.25 (fine) thread has a 1.25mm pitch. This distinction is critical in applications that require high precision and strength. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) simplifies metric thread callouts for coarse threads by eliminating the pitch callout. So, a thread labeled “M10” implies a coarse pitch by default. Any added pitch callout, like M10x1.25, indicates a non-coarse pitch. This ISO standardization dramatically aids in reducing confusion and errors in the manufacturing process.
Using that method, what does the designation M16x2 indicate? According to ISO standards, the pitch callout is eliminated because the thread type is coarse, so M16x2 is designated as “M16.” This simplification helps avoid miscommunication in global manufacturing contexts.
What is the Difference Between Metric and Inch Threads?
The fundamental difference lies in measurement units. Metric threads are measured in millimeters between each thread, whereas inch threads are measured in inches. This distinction is more than just a matter of units; it affects the thread’s fit, strength, and application suitability. Beyond their measurement units, metric and inch threads have a few other key differences:
- Thread Form & Angle: The metric thread is standardized with a 60-degree thread angle, while inch threads, particularly those conforming to the Unified Thread Standard (UTS), have various thread angles, most commonly 60 degrees but sometimes 55 degrees (as in the case of British Standard Whitworth threads). This variation affects how the threads meet and the strength of the connection.
- Tolerance & Fit: Metric threads often adhere to ISO standards that define thread dimensions, tolerances, and fits. These standards ensure consistent quality and compatibility across components, which is crucial in global manufacturing. Inch threads, typically following the Unified Thread Standard, also have their tolerances and fits. Still, these may differ from the ISO standards, affecting interchangeability and compatibility.
- Strength & Precision: Metric threads are typically available in finer pitch measurements, often making them better for applications requiring higher precision and strength. Finer threads provide greater resistance to stripping and allow for more precise tension adjustments. However, with their variable pitch and angle options, inch threads offer flexibility for various strength requirements and material types.
ANSI Equivalents for ISO Thread Sizes
While ISO standards are widely accepted, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) requires pitch callouts for coarse threads. Carr Lane Manufacturing operates globally, so we adhere to ISO standards for metric thread callouts. To bridge the gap between ANSI and ISO and ensure clarity and consistency in international communications, we provide a table that aligns ANSI equivalent callouts with ISO thread sizes. You can review this table at the top of the page, or click here.
When to Use Inch, Metric, and ISO Thread Sizes
Selecting the appropriate thread size and standard is crucial for ensuring compatibility, performance, and durability in engineering and manufacturing. The choice between inch, metric, and ISO thread sizes depends on several factors, including industry standards, geographic location, and specific application requirements. Here's a guide to help you determine when to use each type of thread size:
Inch Sizes
- Geographic Preference: Inch threads are predominantly used in the United States and a few other countries where the imperial system is still in place. They are standard in industries and applications that adhere to U.S. customary units.
- Compatibility: Ideal for replacement parts or assemblies originally designed with inch threads. This ensures that new components are compatible with existing equipment or infrastructure.
- Industry Applications: Common in automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors in the U.S., where traditional engineering practices favor imperial measurements.
Metric Sizes
- Global Standard: Metric threads are widely used outside of the United States, especially in Europe, Asia, and international markets. They are the standard in countries that use the metric system.
- Versatility: Metric threads come in a comprehensive range of sizes and pitches, making them suitable for diverse applications, from fine electronics to large-scale construction.
- Industry Applications: Predominant in automotive, electronics, and general manufacturing industries globally. They are also increasingly adopted by multinational companies to maintain consistency across international operations.
ISO Sizes
- International Compatibility: ISO thread standards are designed to harmonize inch and metric threads, providing specifications that ensure compatibility and interoperability worldwide.
- Precision and Quality: ISO standards often specify tighter tolerances and more rigorous testing, making ISO thread sizes suitable for high-precision applications in aerospace, scientific instrumentation, and high-tech sectors.
- Adaptability: ISO thread sizes are beneficial for companies operating in multiple countries or looking to export products internationally, as they adhere to widely accepted international standards.
Calculate Your Thread Size with Carr Lane Mfg.
Carr Lane Mfg. has an online thread calculator to help you quickly and accurately calculate critical thread dimensions. It supports many thread types and sizes, including internal threads, unified and metric sizes, and screw threads. Using the tool, you can input your desired thread parameters to determine the best thread dimensions and measurements for your application. Access our simple online calculator to make the best decisions for your next project.
Use the Thread Calculator
Use Calculator